- Blog
- What Is Face Symmetry? Complete Guide to Facial Symmetry [2026]
What Is Face Symmetry? Complete Guide to Facial Symmetry [2026]
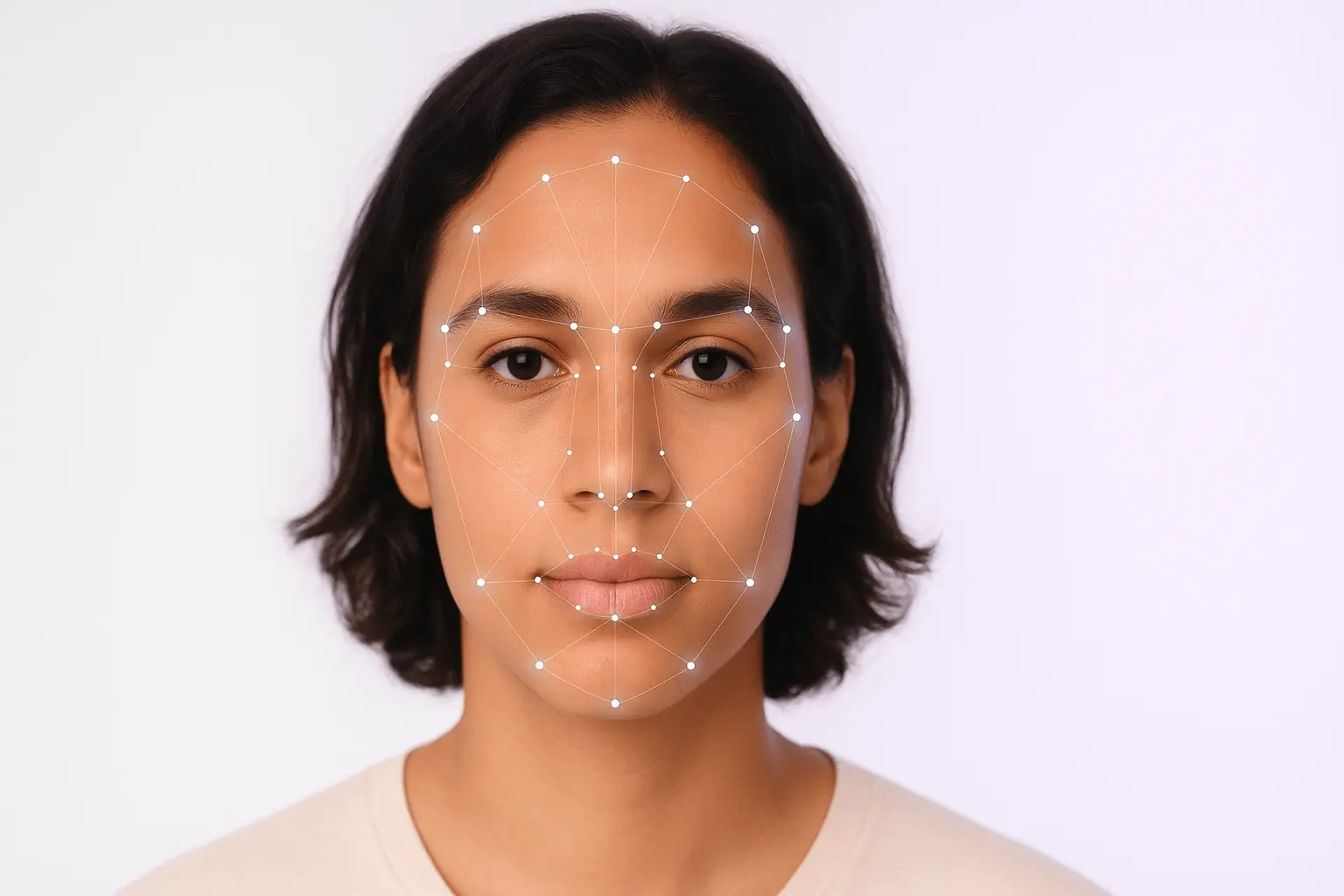 What is face symmetry
What is face symmetry
Ever wondered why certain faces seem universally attractive? The answer often lies in facial symmetry. Whether you're curious about your own symmetry percentage or questioning if perfect symmetry truly equals beauty, this comprehensive guide covers everything you need to know about face symmetry in 2025.
What Is Face Symmetry?
Face symmetry refers to the degree to which one side of your face mirrors the other. In scientific terms, it's the balanced proportion and alignment of facial features when divided by an imaginary vertical line down the center of your face.
Definition and Types of Facial Symmetry
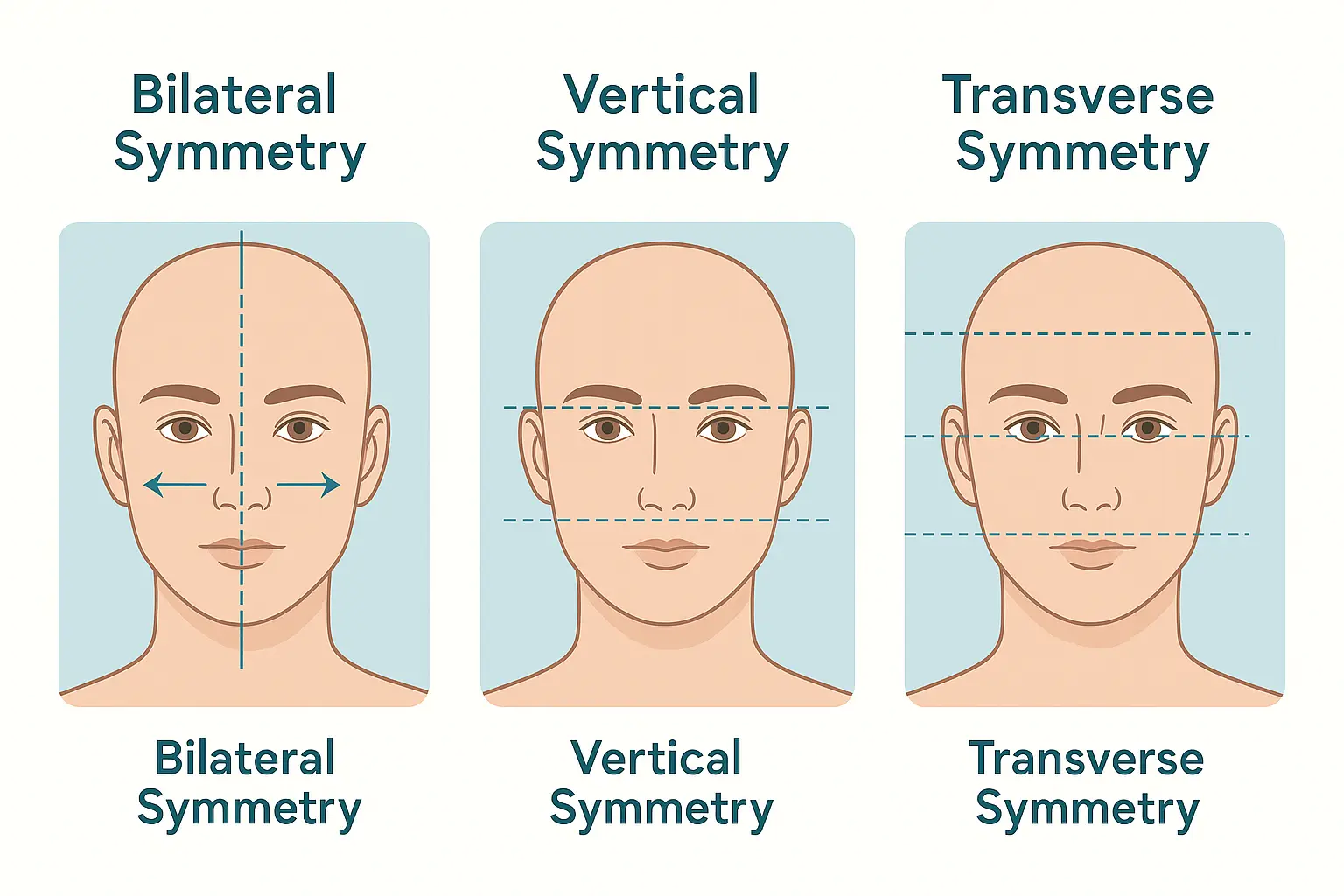 Three Types of Facial Symmetry
Three Types of Facial Symmetry
There are three main types of facial symmetry:
1. Bilateral Symmetry (Left-Right) This is the most commonly discussed type. It measures how closely the left side of your face matches the right side. Key measurement points include:
- Distance between pupils
- Cheekbone prominence
- Jawline angles
- Ear positioning
- Nostril alignment
2. Vertical Symmetry (Upper-Lower) Less commonly analyzed but equally important, this measures the proportional balance between the upper face (forehead to nose) and lower face (nose to chin).
3. Transverse Symmetry This examines the horizontal proportions across different facial planes, though it's typically only assessed in professional medical contexts.
How Is Facial Symmetry Measured?
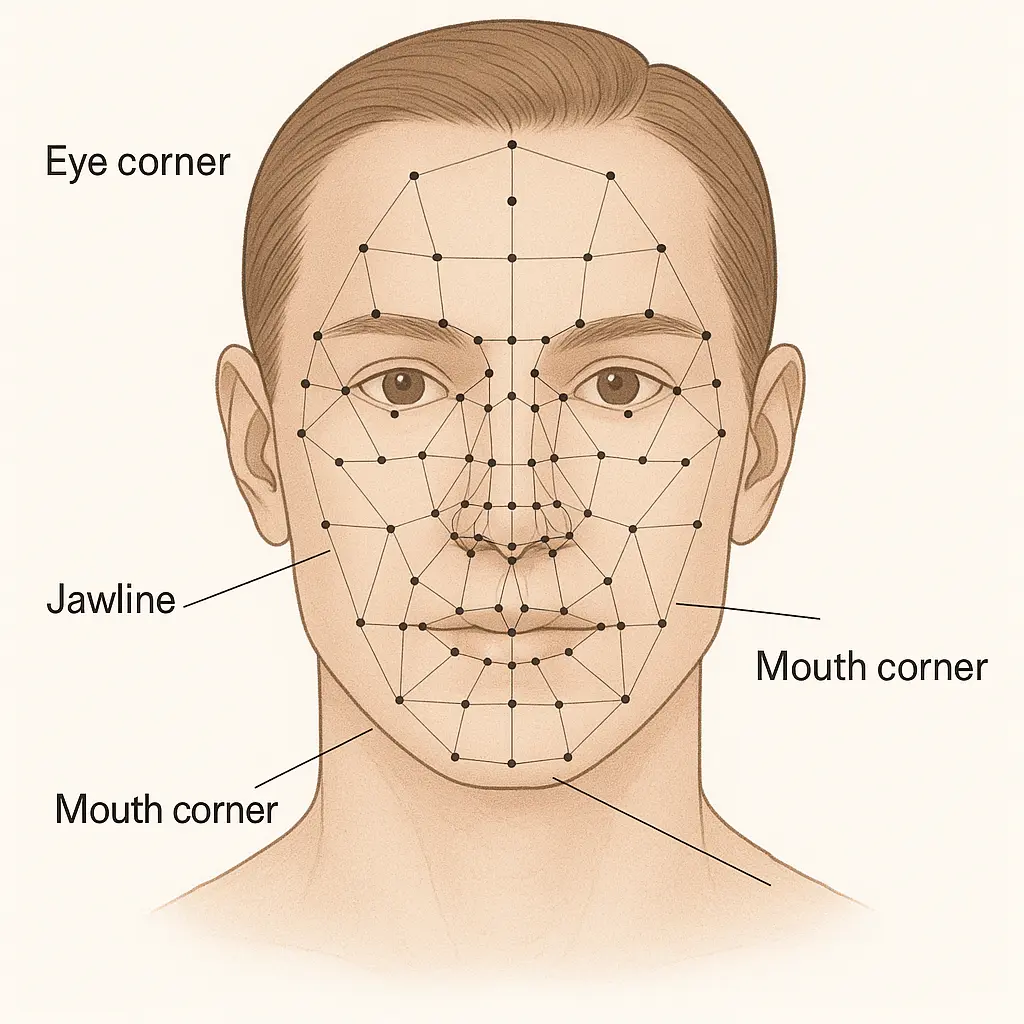 68 Facial Landmarks
68 Facial Landmarks
Professional measurements use:
- 3D facial scanning technology - Creates detailed maps of facial contours
- Photogrammetry - Uses multiple photographs to calculate precise measurements
- Anthropometric analysis - Manual measurements of specific facial landmarks
Modern online tools (like our Face Symmetry Test) use AI-powered algorithms to analyze uploaded photos, comparing key facial landmarks and calculating a symmetry percentage score.
The measurement process typically identifies 68+ facial landmarks including:
- Inner and outer eye corners
- Nose tip and wing positions
- Mouth corners
- Jawline points
- Cheekbone peaks
What Is Meant by Facial Symmetry?
When experts discuss facial symmetry, they're referencing both biological and cultural concepts that have fascinated humans for centuries.
Scientific Perspective: Evolution and Health
From an evolutionary psychology standpoint, facial symmetry serves as a biological indicator. Research suggests that symmetrical faces may signal:
- Genetic quality - Better resistance to genetic mutations
- Developmental stability - Fewer disruptions during growth
- Immune system strength - Better ability to fight off diseases during development
- Reproductive fitness - Historically considered a marker of healthy genes
Multiple studies, including the famous 1994 research by Grammer and Thornhill, found that faces rated as more symmetrical were consistently judged as more attractive across different cultures. - Pub Med
Cultural and Historical Views
The appreciation for symmetry isn't new. Ancient Greek sculptors used mathematical ratios to create "ideal" faces, and Renaissance artists like Leonardo da Vinci studied facial proportions extensively.
Was Marilyn Monroe's face symmetrical? Contrary to popular belief, Marilyn Monroe's face had an asymmetry score of approximately 89% - not perfectly symmetrical. Her slightly uneven smile and asymmetrical eyes actually contributed to her unique charm, proving that perfect symmetry isn't necessary for extraordinary beauty.
Different cultures emphasize symmetry to varying degrees:
- Western cultures tend to place high value on facial symmetry
- Some Eastern cultures consider slight asymmetry as adding character
- Modern beauty standards are gradually embracing natural asymmetry
How to Check Your Face Symmetry
Curious about your own facial symmetry? Here are the methods available, from professional to DIY approaches.
Professional Methods
Medical 3D Scanning ($200-$500)
- Used by plastic surgeons and orthodontists
- Provides millimeter-accurate measurements
- Creates heat maps showing asymmetric areas
Professional Photography Analysis ($50-$150)
- Specialized photographers use calibrated equipment
- Multiple angles captured with consistent lighting
- Software analysis of facial landmarks
Online Tools: Instant and Free
The easiest way to check your face symmetry is using our Face Symmetry Test Tool. Here's how it works:
- Upload a clear, front-facing photo
- AI analyzes 68+ facial landmarks
- Instantly receive your symmetry percentage
- View a detailed breakdown of symmetrical and asymmetrical areas
The tool provides:
- Overall symmetry score (percentage)
- Heat map visualization
- Specific areas of asymmetry
- Comparison to average populations
DIY Method: The Mirror Test
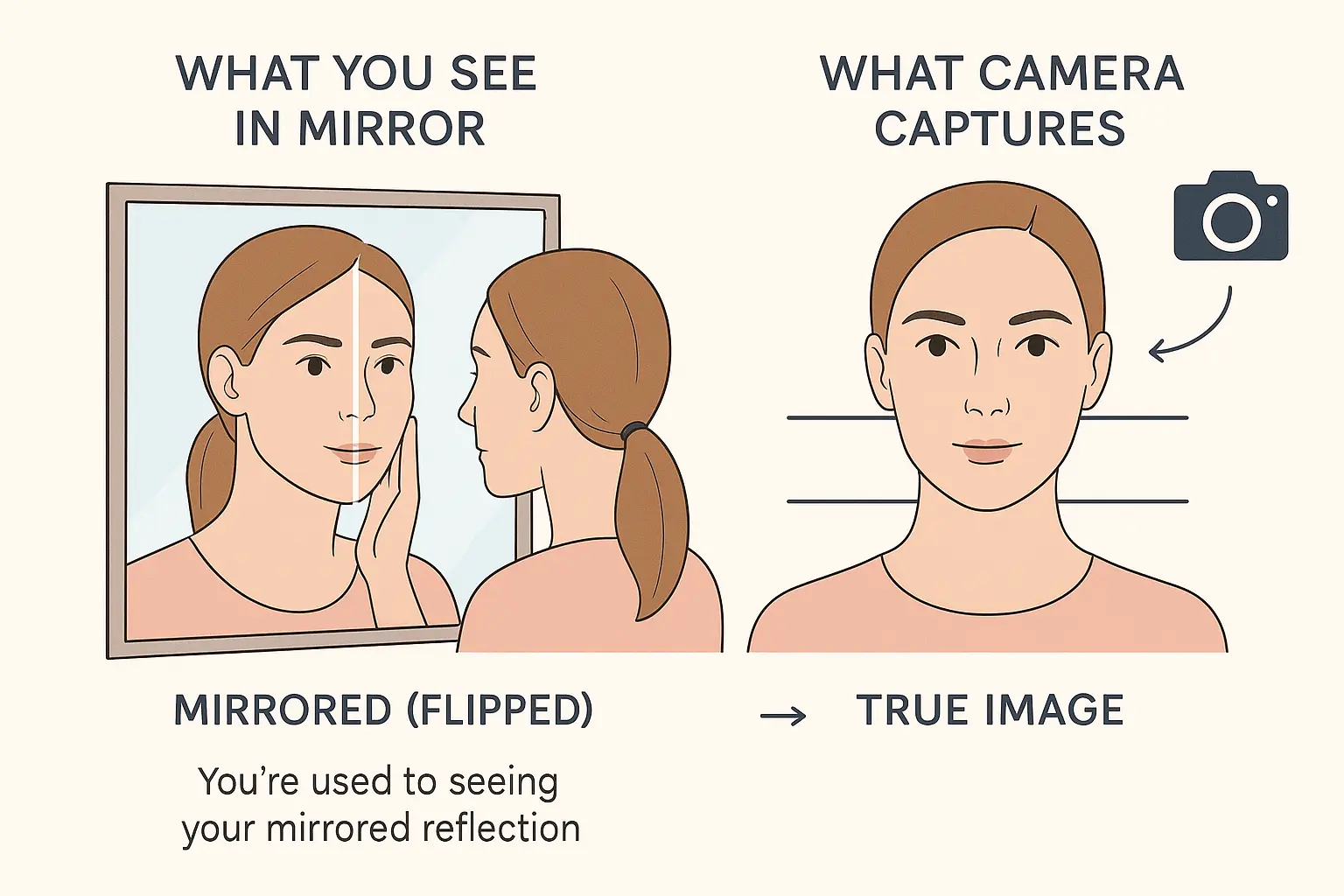 Mirror vs Camera Effect
Mirror vs Camera Effect
While less accurate, you can do a basic assessment at home:
- Take a front-facing photo in good, even lighting
- Use a photo editing app to split your face down the center
- Mirror each half to create two "full faces"
- Compare the mirrored versions to your original photo
Why does my face look lopsided when I take pictures?
This is one of the most common concerns! Here's why:
- Mirror familiarity - You're used to seeing your mirrored reflection, so photos showing the "true" you look strange
- Lens distortion - Phone cameras, especially selfie mode, can distort facial features
- Angle matters - Even slight tilts can exaggerate asymmetry
- Focal length - Wide-angle lenses (common in phones) distort facial proportions
- Lighting shadows - Uneven lighting creates illusions of asymmetry
Professional photographers use 50mm lenses at 5-6 feet distance for the most accurate facial representations.
Want to understand this phenomenon in depth? Read our complete guide on why your face looks different in photos vs mirrors — including the science behind camera distortion and 5 practical steps to finally see your true face.
Understanding Your Face Symmetry Score
Once you've tested your facial symmetry, what does your score actually mean?
What Is a Good Face Symmetry Percentage?
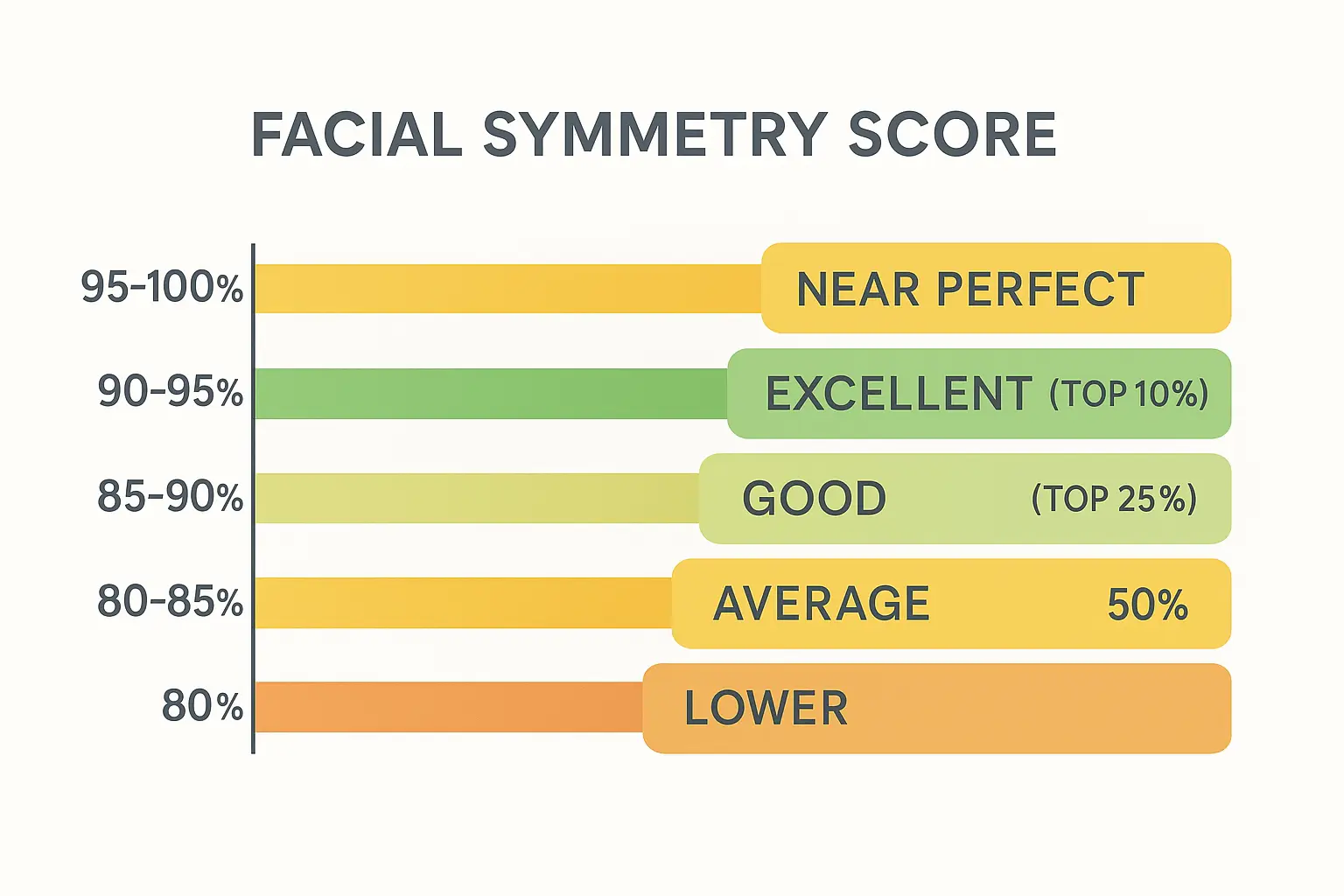 Facial Symmetry Score
Facial Symmetry Score
Here's the breakdown based on research data:
95-100%: Near-Perfect Symmetry
- Extremely rare (less than 1% of the population)
- May actually look slightly "uncanny" or artificial
- Often appears in heavily edited photos rather than real faces
90-95%: Excellent Symmetry
- Top 5-10% of population
- Considered highly attractive by most standards
- Natural-looking and balanced
85-90%: Good Symmetry
- Top 25% of population
- Well-balanced facial features
- Generally perceived as attractive
80-85%: Average Symmetry
- Where most people (50-60%) fall
- Normal, healthy facial development
- Symmetry not immediately noticeable either way
Below 80%: Lower Symmetry
- May have noticeable asymmetric features
- Often due to developmental factors or injuries
- Remember: Beauty involves many factors beyond symmetry
Is 98% Face Symmetry Good?
Yes, 98% face symmetry is exceptional! This score places you in the top 2-3% of the population. However, it's important to understand that:
- Even at 98%, you still have subtle asymmetries (completely normal!)
- This high score suggests very balanced facial development
- Studies show the "sweet spot" for attractiveness is actually 90-95%
- You might have features that are so symmetrical they're approaching the "too perfect" threshold
What Is the Most Attractive Face Symmetry?
Research consistently shows that 90-95% symmetry is rated as most attractive. Why not higher?
- Perfect (100%) symmetry can trigger the "uncanny valley" effect
- Slight asymmetries add character and uniqueness
- Natural facial expressions require some asymmetry
- Perfectly symmetrical faces may seem artificial or computer-generated
Real-World Celebrity Examples
Here are approximate symmetry scores of famous faces:
- George Clooney: ~91% - consistently rated highly attractive
- Scarlett Johansson: ~89% - features slight asymmetry that adds appeal
- Idris Elba: ~92% - strong symmetrical features
- Angelina Jolie: ~88% - distinctive beauty despite imperfect symmetry
- Ryan Gosling: ~90% - balanced, symmetrical features
The pattern? Most celebrities considered extremely attractive fall in the 88-93% range, not at perfect 100%.
Face Symmetry and Attractiveness
The relationship between symmetry and beauty is more nuanced than "more symmetry = more attractive."
The Science Behind Symmetry and Beauty
Multiple peer-reviewed studies have examined this connection:
The 1994 Thornhill and Gangestad Study found that faces with higher symmetry were:
- Rated as more attractive by 85% of participants
- Associated with perceived health and vitality
- Linked to assumptions about personality traits
The 2001 Rhodes Study discovered:
- Symmetry accounts for about 20% of attractiveness ratings
- Other factors (skin quality, facial features, expression) matter more
- Cultural context influences symmetry preferences
Modern Meta-Analysis (2020) concluded:
- Symmetry has a small but consistent effect on attractiveness
- The effect is stronger for body symmetry than face symmetry
- Individual facial features can override symmetry concerns
The Golden Ratio Connection
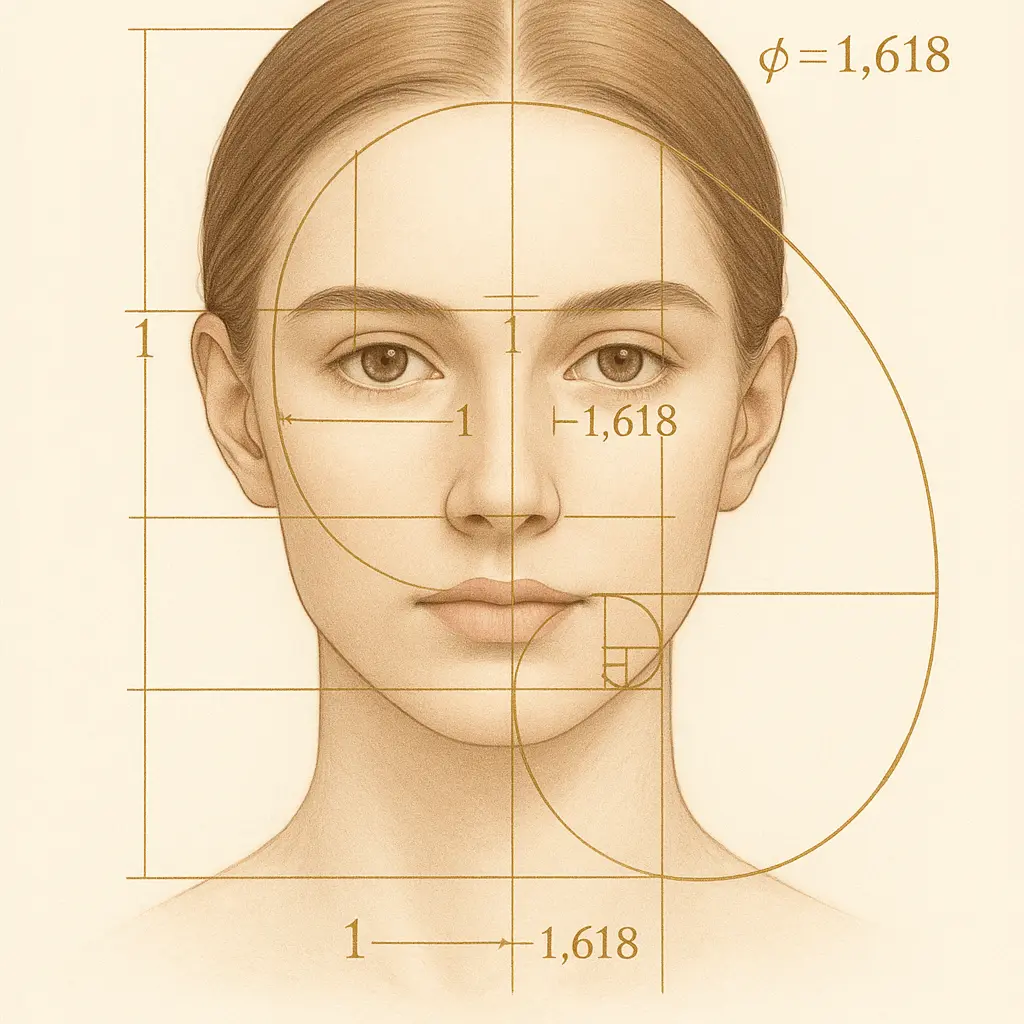 Golden Ratio in Facial Beauty
Golden Ratio in Facial Beauty
The Golden Ratio (1.618:1), also called Phi, appears throughout nature and has been applied to facial beauty analysis:
Key Golden Ratio measurements:
- Face length to width ratio
- Distance between eyes to nose width
- Mouth width to nose width
- Face height divisions
However, modern research shows that strict adherence to the Golden Ratio doesn't necessarily predict attractiveness ratings.
The Sweet Spot: Not Too Perfect
Here's a fascinating finding: faces that are too symmetrical can be perceived as:
- Unnatural or computer-generated
- Less trustworthy (triggering uncanny valley response)
- Lacking character or memorability
- Oddly artificial
This is why:
- Minor asymmetries make faces more interesting
- Imperfections can become signature features (think Cindy Crawford's mole)
- Expressiveness requires some asymmetry
- Perfect symmetry can seem "lifeless"
Perhaps the most important message about facial symmetry comes not from scientific journals, but from real people sharing their experiences. As one Reddit user perfectly expressed in r/AskWomen:
"Not many have symmetrical faces and studies say people with asymmetric faces tend to be more attractive or something like that. But I just remind myself that asymmetric faces are very common, most people don't even realize. So if you're using your phone to obsess over it and keep taking pictures and go on apps to show you how your face would be symmetrical you really need to stop because no one is going to notice those things. Also remind yourself that you're not a doll or a cartoon character, you're real life."
Cultural Perspectives on Beauty
Symmetry preferences vary across cultures:
Western cultures:
- Higher emphasis on facial symmetry
- Strong influence of classical Greek ideals
- Magazine and media reinforcement of symmetrical beauty
Eastern cultures:
- Balance (including symmetry) is valued
- But "interesting" faces with character are also celebrated
- K-beauty and J-beauty trends embrace diverse beauty standards
Contemporary shift:
- Social media is diversifying beauty standards
- "Unique" features gaining appreciation
- Body positivity movement challenging symmetry obsession
Common Causes of Facial Asymmetry
Understanding why asymmetry occurs can help you contextualize your own facial features.
Genetic Factors (Primary Cause)
The most significant factor in facial symmetry is genetics:
- Inherited facial structure - Bone structure patterns from parents
- Developmental genes - Control how features grow and align
- Ethnic background - Different populations have varying average symmetry levels
- Family traits - Asymmetrical features often run in families
Research shows that facial asymmetry is 50-60% heritable, meaning genetics play a major role but aren't the only factor.
Eye asymmetry:
One of the most common genetic asymmetries is having eyes that appear different sizes. In most cases, the eyes themselves are the same size—it's the eyelids, brow position, or surrounding tissue that creates the illusion of difference. This is completely normal and affects the vast majority of people.
Concerned about uneven eyes? You're not alone—it's one of the top searched facial asymmetry topics. Learn what causes it and when to seek help: Why Is One Eye Bigger Than the Other?
Developmental and Growth Factors
During childhood and adolescence, development can affect symmetry:
Prenatal development:
- Nutritional factors during pregnancy
- Positioning in the womb
- Birth complications or trauma
Childhood growth:
- Uneven growth spurts
- Dental development
- Jaw growth patterns
- Hormonal influences during puberty
Dental and orthodontic issues:
- Crossbites and malocclusions
- Missing teeth causing compensatory growth
- TMJ (temporomandibular joint) disorders
Braces and orthodontic treatment:
- Correcting bite alignment can subtly change jaw position and facial profile
- Most noticeable in growing teenagers; effects are more limited in adults
- Primarily affects lower face proportions, not upper facial symmetry
Many people wonder if getting braces will change their face shape. The answer depends on your age, bite type, and treatment plan. Learn more: Do Braces Change Your Jawline?
Wisdom teeth and extraction:
- Impacted wisdom teeth can push other teeth and affect jaw alignment
- Extraction may cause subtle bone remodeling, but effect on appearance is usually minimal
- Swelling after removal is temporary, not permanent facial change
Will removing your wisdom teeth slim down your face? It's one of the most common questions about facial changes. Get the full answer: Does Removing Wisdom Teeth Change Your Jawline?
Lifestyle Habits That Cause Asymmetry
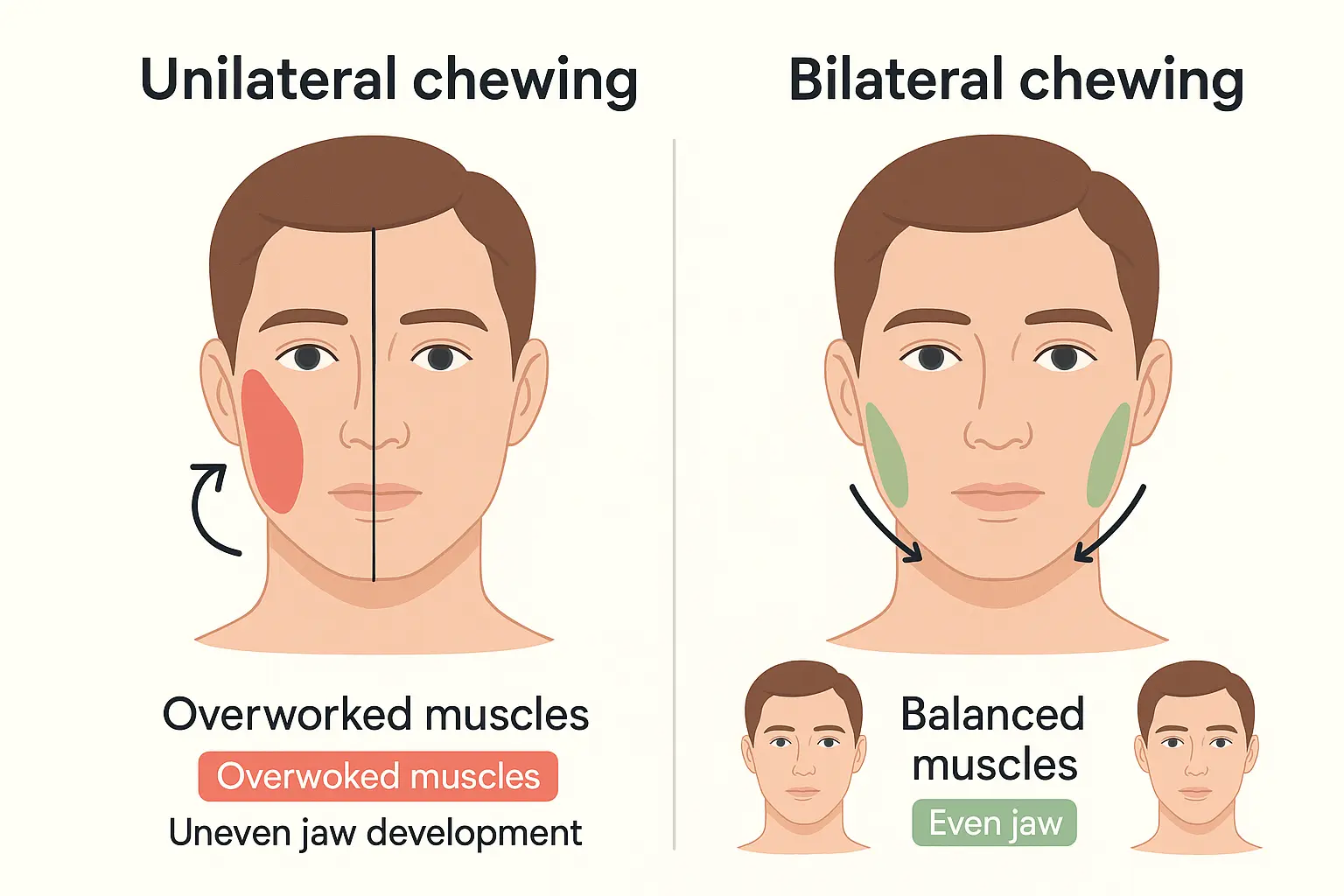 Chewing Habits and Facial Symmetry
Chewing Habits and Facial Symmetry
Daily habits can gradually increase facial asymmetry:
Chewing patterns:
- Consistently chewing on one side wears down teeth unevenly
- Causes stronger muscle development on the favored side
- Can lead to jaw misalignment over years
Research in orthodontics has demonstrated that habitual unilateral (one-sided) chewing can lead to asymmetric development of masticatory muscles and even affect jaw bone structure over time. The consistently-used side develops stronger muscles and may show altered bone remodeling. - ScienceDirect
Sleeping positions: One of the most underestimated factors! Sleeping consistently on one side can:
- Compress facial tissues on that side
- Create fluid drainage patterns
- Cause temporary morning asymmetry
- Over decades, potentially affect bone structure
Can sleeping position affect asymmetry? Yes! Studies show that side-sleepers often develop slight asymmetries on their favored side. The constant pressure can:
- Flatten cheekbones slightly
- Create differences in facial fat distribution
- Affect skin texture and elasticity unevenly
Facial habits:
- Resting chin on hand (compresses one side)
- Habitual facial expressions (raising one eyebrow)
- Sun exposure asymmetry (driver's side sun damage)
Injuries and Medical Factors
Physical trauma can create or worsen asymmetry:
- Broken nose or jaw
- Facial nerve damage
- Stroke (can cause facial paralysis on one side)
- Bell's palsy (temporary facial paralysis)
- Previous surgeries or accidents
Nasal injuries and crooked nose:
A crooked nose is one of the most visible forms of facial asymmetry, and it's often the result of injury—whether from sports, accidents, or even childhood falls you might not remember. In some cases, a deviated septum (the internal wall of the nose) can also make the nose appear crooked from the outside.
Not sure if your crooked nose is cosmetic or a breathing issue? There's an important difference. Get the complete breakdown: Why Is My Nose Crooked?
Aging Process
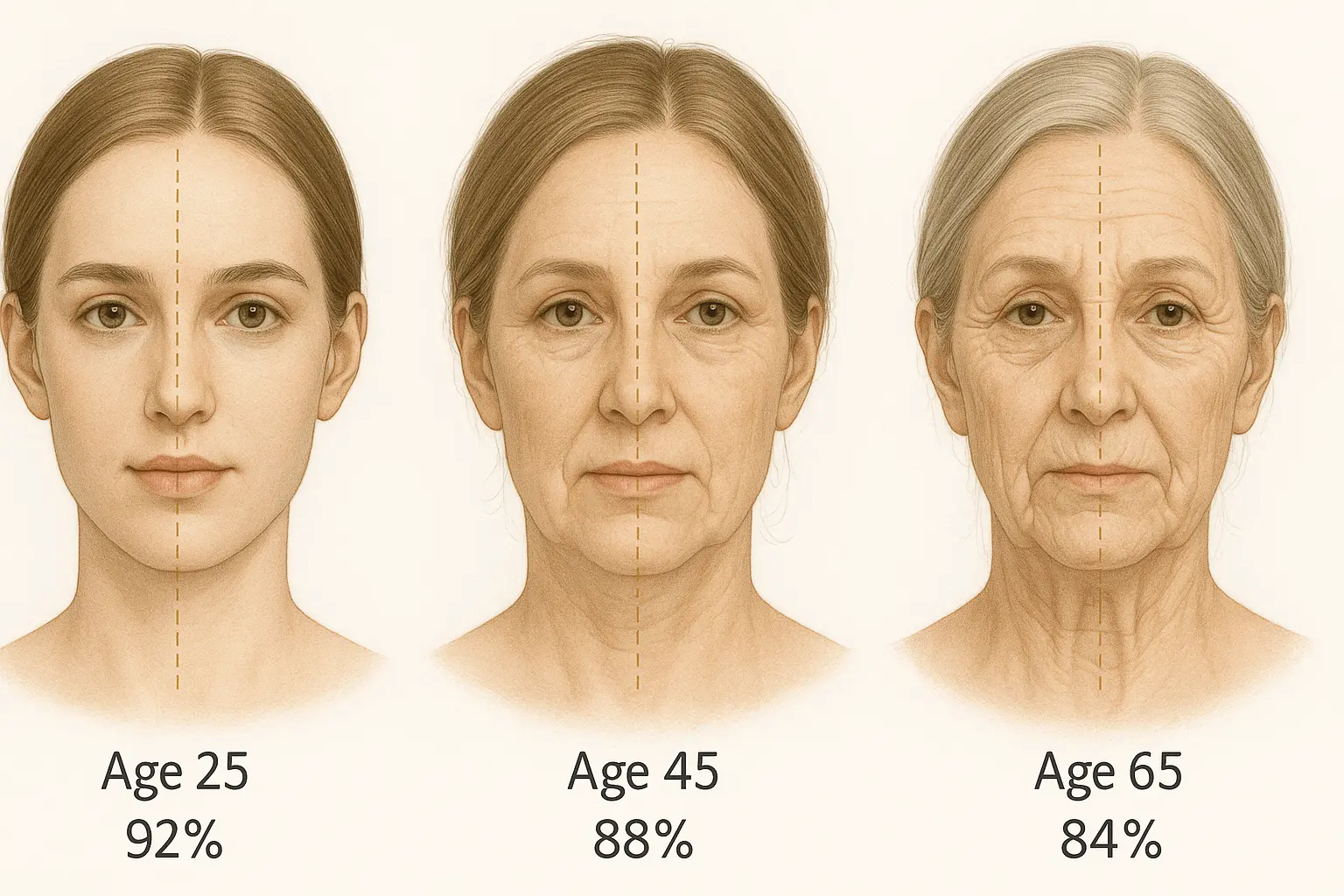 How Aging Affects Facial Symmetry
How Aging Affects Facial Symmetry
Aging affects facial symmetry:
Natural aging changes:
- Bone resorption (uneven bone loss)
- Fat pad migration (moves downward and asymmetrically)
- Muscle tone differences (if you use one side more)
- Skin elasticity loss (gravity affects faces unevenly)
Lifestyle-accelerated aging:
- Sun damage (usually asymmetrical)
- Smoking (affects circulation unevenly)
- Repeated expressions (smile lines, frown lines)
Uneven fat distribution:
One of the most common aging concerns is noticing that one side of your face looks fuller or heavier than the other. This happens because fat pads don't shrink or shift at the same rate on both sides. Genetics, sleeping habits, and even which side you chew on can influence how fat distributes across your face over time.
Wondering why one cheek looks bigger? It's more common than you think. Read the full breakdown: Why Is One Side of My Face Fatter?
Can Diet Affect Facial Symmetry?
While diet doesn't directly change bone structure, it can influence facial appearance:
Sodium intake:
- High sodium causes water retention
- May cause asymmetric facial puffiness
- Temporary effect, not permanent structure change
Alcohol and facial bloating:
Alcohol is another major cause of temporary facial puffiness. It dehydrates your body, causing it to retain water—often unevenly across your face. A night of drinking can make one side of your face look noticeably puffier the next morning, and regular alcohol consumption can lead to chronic facial bloating.
Want to know exactly how alcohol affects your face and how to reverse the puffiness? Read: Does Alcohol Make Your Face Puffy?
Nutrition during development:
- Deficiencies during childhood can affect growth
- Vitamin D and calcium crucial for bone development
- Protein necessary for muscle development
Rapid weight loss and "Ozempic Face":
With the rise of GLP-1 medications like Ozempic and Wegovy for weight loss, a new concern has emerged: "Ozempic face." Rapid weight loss can cause facial fat to disappear faster than the skin can adjust, leading to a gaunt, aged appearance with sagging and loss of facial volume. This can also make existing asymmetries more pronounced.
Considering weight loss medication or a strict diet? Learn how to protect your facial appearance: How to Avoid Ozempic Face
For a complete guide on managing facial fat and puffiness, read: How to Decrease Face Fat.
Can a Face Be 100% Symmetrical?
This is one of the most searched questions, so let's address it directly.
The Truth About Perfect Symmetry
Short answer: Extremely rare, and probably not desirable.
Here's the reality:
Why 100% symmetry is virtually impossible:
- The human body isn't designed to be perfectly symmetrical
- Even identical twins have different symmetry levels
- Micro-movements during development create variations
- Environmental factors (womb position, sleeping) affect development
- Internal organs aren't symmetrical, influencing skeletal structure
Research findings:
- Less than 0.1% of people have >99% facial symmetry
- Those who do often have some artificial enhancement
- Genetic or developmental anomalies would be needed for perfect symmetry
This phenomenon is related to the "uncanny valley" effect, first described by roboticist Masahiro Mori in 1970. Research has shown that perfectly symmetrical faces can trigger this response, making them appear artificial or unsettling despite their technical "perfection." - ResearchGate
Who Has a 100% Symmetrical Face?
The honest answer: Probably no one naturally.
Claims of perfect symmetry usually involve:
- AI-generated faces (not real people)
- Heavily edited photographs
- Misunderstanding of measurement methods
- Marketing by cosmetic procedures
What about "perfectly symmetrical" celebrities? When you see articles claiming someone has a "perfectly symmetrical face," they usually mean:
- High symmetry (93-96% range)
- Well-balanced features
- Aesthetically pleasing proportions
Even celebrities known for symmetry have imperfections:
- Denzel Washington: ~91-93%
- Florence Pugh: ~89-92%
- Michael B. Jordan: ~90-93%
Is Perfect Symmetry More Attractive?
Counterintuitively, no. Research consistently shows:
The "Uncanny Valley" Effect:
- Perfectly symmetrical faces can appear unnatural
- Human brains are attuned to detect "too perfect" features
- May trigger discomfort or distrust
- Often associated with AI or CGI faces
What makes faces attractive:
- Balance, not perfection (90-95% symmetry sweet spot)
- Distinct features (memorable characteristics)
- Expression and animation (requires some asymmetry)
- Skin quality and health (often more important than structure)
- Confidence and personality (how you carry yourself)
Real-world experiment: Studies where researchers created perfectly symmetrical versions of real faces found:
- Original faces (with natural asymmetry) were often rated as more attractive
- Perfectly symmetrical versions seemed "off" or "fake"
- Personality seemed less readable in symmetrical versions
Which Facial Symmetry Is Attractive?
The most attractive faces typically show:
- 90-94% overall symmetry - high enough to signal health
- Balanced proportions - even if not perfectly symmetrical
- Distinctive features - slight asymmetries that create character
- Natural expression capability - requires some muscle asymmetry
How to Improve Face Symmetry
While this article focuses on understanding facial symmetry, many people wonder if asymmetry can be improved. Here's a brief overview:
Natural Approaches
Lifestyle adjustments:
- Facial exercises and mewing techniques
- Correcting sleeping position (try back-sleeping)
- Balancing chewing habits (use both sides equally)
- Facial massage and lymphatic drainage
- Posture improvement (affects jaw alignment)
Habits to develop:
- Alternate sides when sleeping
- Avoid resting chin on hand
- Chew evenly on both sides
- Practice symmetrical facial expressions
Professional Options
Non-invasive treatments:
- Orthodontic work (corrects dental asymmetry)
- Physical therapy (for TMJ and muscle issues)
- Dermal fillers (temporary volumizing)
- Botox (relaxes overactive muscles)
Surgical procedures:
- Jaw surgery (for significant structural issues)
- Rhinoplasty (nose reshaping)
- Chin or cheek implants (severe cases only)
→ For detailed, step-by-step methods to improve facial symmetry, read our comprehensive guide: How to Fix Face Asymmetry
The guide covers:
- Specific facial exercises with illustrations
- Sleeping position optimization
- Professional treatment comparisons
- Realistic timeline expectations
- When to see a specialist
Is a Symmetrical Face Healthy?
Facial symmetry has long been considered a marker of health, but what does science actually say?
Symmetry as a Health Indicator
Evolutionary biology perspective: Symmetry is thought to indicate:
- Fewer genetic mutations during development
- Better resistance to environmental stressors
- Stronger immune system during growth
- Efficient metabolic processes
What research shows:
- Correlation exists but is weaker than once thought
- Symmetry predicts health better in extreme cases
- Modern medicine makes this marker less relevant
- Many healthy people have asymmetrical faces
Is an Asymmetrical Face Healthy?
Yes! Asymmetry is normal and usually healthy.
Most facial asymmetry is:
- Completely benign
- Result of normal development variations
- Not associated with health problems
- More about aesthetics than medical concern
When to See a Medical Professional
Consult a doctor if:
- Sudden asymmetry develops (possible stroke or nerve damage)
- Asymmetry worsens rapidly
- Accompanied by pain, numbness, or difficulty moving face
- One-sided facial drooping occurs
- Following trauma or injury
- Affects ability to eat, speak, or breathe
Medical conditions that can cause asymmetry:
- Bell's palsy (temporary facial paralysis)
- Stroke (requires emergency care)
- TMJ disorders (jaw joint problems)
- Dental infections or abscesses
- Tumors (rare)
- Congenital conditions (present from birth)
Test Your Face Symmetry Now
Ready to discover your facial symmetry percentage? Use our free Face Symmetry Test tool to get instant results.
What you'll receive:
- Precise symmetry percentage score
- Visual heat map of your face
- Identification of asymmetric areas
- Comparison to population averages
- Personalized insights
The test takes less than 30 seconds and requires only a clear, front-facing photo. No signup or personal information needed!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the rarest face shape?
The diamond face shape is considered the rarest, occurring in less than 5% of the population. It features high, prominent cheekbones with a narrow forehead and jawline. Regarding symmetry, face shape doesn't directly determine symmetry levels - all face shapes can have high or low symmetry.
Does sleeping position affect asymmetry?
Yes! Consistently sleeping on one side can contribute to facial asymmetry over time. The constant pressure compresses facial tissues, affects fluid drainage, and may influence bone structure after decades. Back-sleeping is ideal for maintaining facial symmetry, though stomach-sleeping has the most significant asymmetric effects.
Does facial asymmetry get worse with age?
Generally, yes. Facial asymmetry tends to increase with age due to:
- Uneven bone resorption
- Asymmetric fat loss and redistribution
- Muscle tone differences between sides
- Gravity's uneven effects
- Accumulated effects of habitual expressions
However, the rate and degree vary greatly between individuals. Maintaining healthy habits can slow these changes.
How rare is perfect face symmetry?
True perfect (100%) facial symmetry is extraordinarily rare - likely affecting less than 0.01% of the global population, if anyone. Even symmetry above 98% is found in less than 1% of people. The vast majority of humans fall between 80-95% symmetry, which is completely normal and healthy.
What are the three types of asymmetry?
The three main types of facial asymmetry are:
- Structural asymmetry - Differences in bone structure (jaw, cheekbones, eye sockets)
- Functional asymmetry - Related to muscle use and movement patterns (one side more developed)
- Dental asymmetry - Caused by tooth positioning, bite issues, or jaw alignment problems
Most people have a combination of all three types to varying degrees.
Conclusion
Facial symmetry is a fascinating intersection of biology, psychology, and aesthetics. While symmetry does play a role in how we perceive faces, it's just one factor among many that contribute to attractiveness and individuality.
Key takeaways:
- Perfect symmetry is rare and not necessarily more attractive
- 80-95% symmetry is normal for most people
- The "sweet spot" for attractiveness is 90-95%, not 100%
- Asymmetry is natural, healthy, and often adds character
- Genetics, development, and lifestyle all influence symmetry
- Professional and DIY methods exist to assess your symmetry
Remember: Your unique facial features, including any asymmetries, contribute to what makes you distinctly you. While understanding your facial symmetry can be interesting, it shouldn't define your self-worth or perception of beauty.
Ready to discover your facial symmetry percentage?
And if you're interested in learning how to enhance your facial symmetry through natural methods and professional options, check out our companion guide: